Introduction
It’s easy to undervalue the significance of nutrition Dense Foods in our day-to-day lives in today’s hectic society. Nonetheless, eating the correct nutrients is essential to preserving good health. However, what does eating healthfully really mean? Let’s introduce the idea of foods high in nutrients. These superfoods are loaded with the vitamins, minerals, and other vital elements that our bodies require to function properly.
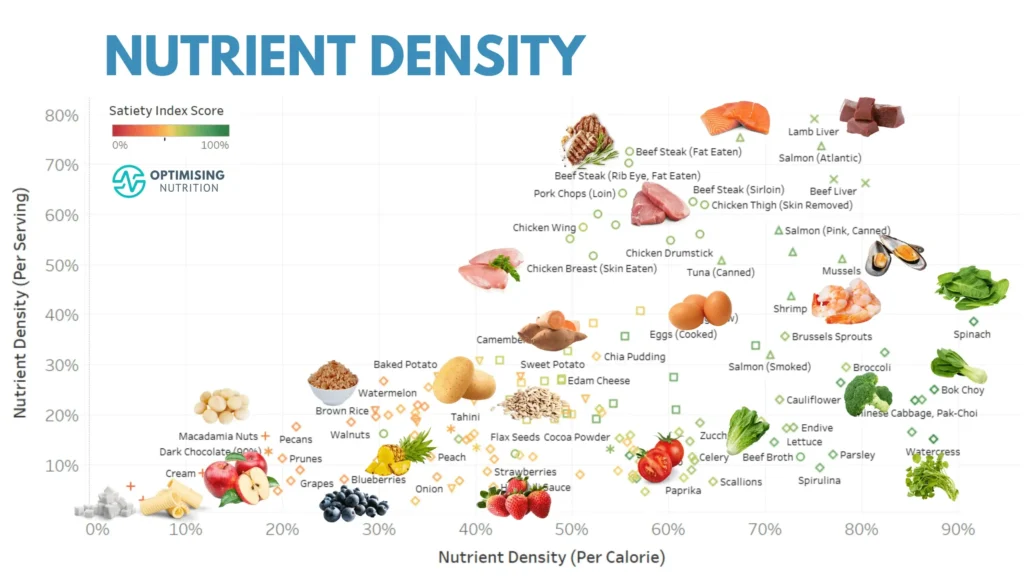
Define Nutrient Density
The concentration of vital elements, such as vitamins, minerals, protein, and fiber, in a given diet with its calorie content is referred to as nutritional density. To put it simply, foods that are abundant in nutrients per calorie are considered to be highly beneficial for maintaining general health and energy.
Importance of Nutrient-Dense Foods
Foods high in nutrients are essential for promoting optimal growth and development, helping people maintain a healthy weight, and lowering their chance of developing chronic illnesses like diabetes, heart disease, and some types of cancer. You can provide your body with the necessary nutrition it needs to perform at its peak by eating a diet high in these nutrients.
Types and Categories
There are many different options available when it comes to nutrient-dense foods. These foods’ nutritional profiles and health advantages allow them to be divided into multiple classes.
Fruits and Vegetables
Among the foods that are high in nutrients are fruits and vegetables. They are abundant in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, all of which are critical for good health. To make sure your diet is providing you with a wide range of nutrients, try to incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables.
Leafy Greens
Vitamins A, C, and K, along with folate, iron, and calcium, are abundant in leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard. To increase the nutrients in salads, smoothies, or sautés, add them.
Berries
In addition to being delicious, berries like raspberries, strawberries, and blueberries are also great sources of fiber and antioxidants. Savor them on their own, blended into smoothies, or combined with yogurt or muesli.
Whole Grains
Minerals including iron, magnesium, and selenium, as well as fiber and B vitamins, can also be found in whole grains. Choose whole grains over refined ones. Quinoa, brown rice, oats, and barley are examples of whole grains that are higher in nutrients.
Quinoa
Quinoa has all nine of the essential amino acids, making it a complete protein. It’s a healthy addition to any meal because it’s abundant in fiber, magnesium, iron, and zinc.
Oats
Soluble fiber, which is abundant in oats, has been shown to decrease cholesterol and promote heart health. Additionally, they are a good source of magnesium, phosphorus, and manganese.
Lean Proteins
Protein is necessary for immune system support, tissue growth and repair, and muscle mass maintenance. Select lean protein sources like lentils, beans, seafood, and tofu to maximize nutrient intake while minimizing the consumption of saturated fat.
Salmon
Omega-3 fatty acids, which are good for heart and brain function, are abundant in salmon. Protein, vitamin D, and B vitamins are also abundant in it.
Lentils
A plant-based source of protein, lentils are also rich in potassium, iron, fiber, and folate. They work well in a variety of dishes, including salads, curries, and soups.

What Are Nutrient-Dense Foods?
Definition and Explanation
Foods that have a high concentration of nutrients in relation to their calorie level are considered nutrient-dense. In terms of nutrition, these items are more affordable than junk food, which contains empty calories.
Examples of Nutrient-Dense Foods
Consider colorful fruits like strawberries and blueberries, lean meats like salmon and chicken breast, and leafy greens like spinach and kale. These meals are nutrient-dense and support many different body functions.
Benefits of Nutrient-Dense Foods
Better Health Outcomes
Consuming foods high in nutrients can improve one’s health. These nutrients lower the risk of chronic diseases and improve heart health as well as immunological function.
Weight Management
Nutrient-rich foods are satisfying and low in empty calories, which makes them beneficial for managing weight. It’s easier to eat more without going overboard when it comes to maintaining or achieving a healthy weight.
Enhanced Energy Levels
Foods high in nutrients provide your body with the energy it needs to function at its peak. These foods’ vitamins and minerals facilitate food’s more effective conversion to energy.
Comparing Nutrient-Dense Foods to Calorie-Dense Foods
Nutrient Density vs. Calorie Density
Foods high in nutrients yet low in calories are said to be nutrient-dense. Conversely, calorie-dense foods, such as fried dishes and sugary snacks, provide a lot of calories but little nutritional benefit.
The Pitfalls of Calorie-Dense Foods
Frequent consumption of high-calorie foods can result in nutritional inadequacies, weight gain, and a higher chance of developing chronic illnesses like diabetes and heart disease.
How to Identify Nutrient-Dense Foods
Reading Nutrition Labels
Finding foods that are high in nutrients requires knowing how to read nutrition labels. Seek out foods that are low in harmful fats and added sugars and abundant in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Recognizing Whole Foods
Fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats are examples of whole foods that are generally higher in nutrients than processed foods. Their nutritious value hasn’t been diminished by processing.
Diagnosis and Tests
Although there aren’t any particular diagnostic tests for determining vitamin intake, medical experts can check nutritional status and spot probable deficiencies using a number of techniques.
Dietary Assessment
Maintaining a food journal or consulting with a qualified dietitian will assist you in evaluating your present eating patterns and pinpointing opportunities for enhancement. You may make educated diet decisions by keeping a food journal and analyzing the nutrients you consume.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can determine the amounts of minerals, including calcium, iron, vitamin D, and B vitamins, in your blood. These tests can aid in determining inadequacies and serve as a basis for suggestions for dietary adjustments or supplements.
The Role of Micronutrients
importance of Vitamins and Minerals
Minerals and vitamins are examples of micronutrients that are essential to many body processes. Among other things, they aid in wound healing, bone health, and immune system function.
Common Micronutrient-Rich Foods
Nuts (source of magnesium), citrus fruits (source of vitamin C), and dairy products (source of calcium) are good places to get important micronutrients.
Nutrient-Dense Foods for Different Diets
Vegan and Vegetarian Options
Excellent nutrient-dense choices for people on a plant-based diet are leafy greens, beans, lentils, and whole grains.
Keto and Low-Carb Choices
For low-carb or ketogenic diets, avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish are ideal because they provide necessary fats and nutrients without being overly carbohydrate-rich.
Gluten-Free Selections
Quinoa, brown rice, sweet potatoes, and a variety of fruits and vegetables can satisfy the nutritional demands of those following a gluten-free diet.
Incorporating Nutrient-Dense Foods into Your Diet
Meal Planning Tips
Eating a healthy diet can be made easier by organizing your meals around nutrient-dense items. Make an effort to include a range of food types and colors in your meals.
Easy and Delicious Recipes
Nutrient-dense meals can be made fun with easy recipes like grilled salmon served with steamed broccoli, a smoothie made with spinach and berries, or a quinoa salad with mixed veggies.
Nutrient-Dense Foods for Specific Health Goals
Foods for Heart Health
Oats, flaxseeds, berries, and fatty salmon are among the foods that are great for heart health because they are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Foods for Brain Health
Leafy greens, walnuts, and blueberries are recognized to promote brain health and enhance memory and cognitive performance.
Foods for Muscle Building
Protein is abundant in lean meats, eggs, dairy products, and legumes. Protein is necessary for both muscle growth and repair.
Symptoms and Signs
Eating a diet high in foods high in nutrients can do a lot for your health and wellbeing. The following indicates that you’re providing your body with the proper nutrition:
Increased Energy Levels
Foods high in nutrients give your body the vital vitamins and minerals it needs to efficiently manufacture energy. It may indicate that your diet is working if you notice that you have more energy during the day.
Improved Digestion
Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are examples of foods high in fiber that improve digestive health by encouraging regular bowel movements and reducing constipation. Your nutrient-dense diet may be to blame if you see benefits in your digestion, such as less bloating or discomfort.
Enhanced Mood and Mental Clarity
Nutrient-dense diets are rich in nutrients, which are essential for cognitive and mental wellness. Focus, mental clarity, and mood stability can all be enhanced by eating a diet high in vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Shopping Tips for Nutrient-Dense Foods
Shopping on a Budget
It’s not always expensive to eat healthily. You can eat nutrient-dense foods on a budget by selecting frozen fruits and vegetables, buying in-season produce, and visiting farmers’ markets.
Choosing Seasonal Produce
As seasonal produce is collected at its optimal maturity, it contains more vitamins and minerals than out-of-season produce and is therefore frequently higher in nutrients.
Common Myths About Nutrient-Dense Foods
Debunking Popular Misconceptions
A common misconception is that nutrient-dense meals are expensive or complicated to prepare. But anyone can easily and economically include these foods in their diet with the appropriate strategy.
Understanding True Nutrition
It’s critical to realize that not all advertised “superfoods” have the health benefits they claim. Real nutrient-dense meals are uncomplicated, complete foods without pretentious labeling.
Causes and Risk Factors
Although there is no denying the advantages of eating foods high in nutrients, a diet low in these vital elements can be caused by a variety of circumstances. You may choose your food and lifestyle more wisely if you are aware of these causes and risk factors.
Processed Foods
Processed foods frequently lack vital nutrients and are heavy in calories, sugar, and bad fats. Overindulging in processed meals can gradually cause dietary deficiencies by replacing more nutrient-dense items in your diet.
Poor Eating Habits
A diet deficient in nutrients can result from skipping meals, eating on the run, and depending too much on convenience foods. Maintaining optimal health requires taking the time to plan and prepare balanced meals with nutrient-dense ingredients.
Restricted Diets
Several dietary limitations, such as being gluten-free or vegan, might make it difficult to get all the vital nutrients your body requires. To make sure you’re getting all the nutrients you need, it’s critical to look for alternate sources of crucial nutrients.
The Environmental Impact of Nutrient-Dense Foods
Sustainability and Food Choices
Selecting meals high in nutrients can also benefit the environment. Producing plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, and grains usually uses less energy than producing animal goods.
Supporting Local Agriculture
Purchasing locally grown vegetables helps local farmers and lessens the carbon impact caused by long-distance food transportation.
Treatment Options
Making dietary adjustments to guarantee you’re receiving a balanced diet rich in vital nutrients is the main treatment for nutritional deficiencies. Supplementation could be advised in some circumstances to address particular inadequacies.
Dietary Changes
Simple dietary adjustments, including eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats, can enhance nutritional intake and promote general health. To make sure you are fulfilling your nutritional needs, put an emphasis on moderation, balance, and diversity.
Supplementation
Supplementation could be required in some circumstances to remedy nutrient deficits that are not sufficiently addressed by food alone. Consult a medical expert to ascertain whether supplementing is suitable for your particular requirements.
Preventive Measures
Developing a nutritious diet that prioritizes foods high in nutrients is the first step toward preventing nutrient shortages. The following advice will help you make sure your body is receiving the nutrition it needs:
Eat a Variety of Foods
To make sure you’re getting a varied range of nutrients, include a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats in your diet.
Conclusion
Including foods high in nutrients in your diet is one of the most effective ways to improve your overall health and well-being. These nutrient-dense meals boost overall health, help you maintain a healthy weight, and give you more energy without packing on the pounds. Making nutrient-dense food choices and understanding them can help you make decisions that are good for the environment and your body.
FAQs
-
What makes a food nutrient-dense?
When a food has a high nutrient content concerning its calorie count, it is said to be nutrient-dense. This covers fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals.
-
Are nutrient-dense foods expensive?
Not always. When purchased in season or in large quantities, several nutrient-dense foods, such as whole grains, legumes, and seasonal fruits and vegetables, can be reasonably priced.
-
Can kids benefit from nutrient-dense foods?
Of course! Nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can help ensure that kids obtain the nutrients they need for healthy growth and development.
-
How do nutrient-dense foods affect aging?
Foods high in nutrients promote general health, which can lead to a healthy aging process. They offer vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can prevent aging-related illnesses and enhance longevity.
-
Are all superfoods nutrient-dense?
Certain promoted “superfoods” aren’t actually that nutrient-dense. It’s critical to concentrate on complete, unprocessed meals that are naturally high in nutrients.

4 thoughts on “We Need to Choose Nutrient-Dense Foods for Our Diet Because”
This post is exactly what I was looking for. You’ve addressed all the questions I had and provided clear, actionable advice.
Thank you
I love how you break things down so clearly.
Thank you